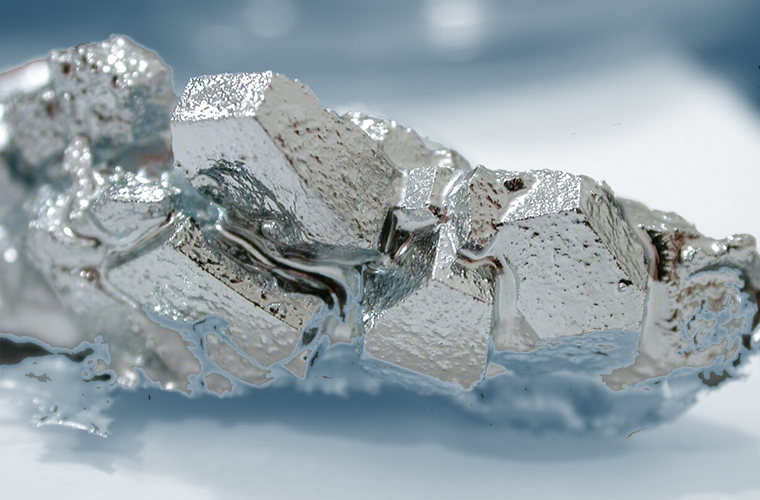
Gallium oxide (Ga2O3)
Gallium oxide (Ga2O3) is a semiconductor material with good chemical and thermal stability. Its bandgap width is 4.7-4.9 eV, critical breakdown field strength is 8 MV/cm (much higher than the theoretical limit of 2.5 MV/cm for SiC and 3.3 MV/cm for GaN), electron mobility is 250 cm2/V • s, and it has strong transparent conductivity. The Barigard value exceeds 3000, which is several times that of GaN and SiC materials.
- Radiation detection sensor chips can be applied in fields such as communication, radar, aerospace, high-speed rail vehicles, and new energy vehicles. Especially in high-power, high-temperature, and high-frequency devices, gallium oxide has greater advantages over silicon carbide and gallium nitride in many aspects.
- Broadband Gap: Gallium oxide has a broadband gap of approximately 4.8 to 4.9 electron volts, making it advantageous in applications such as ultraviolet photodetectors and power devices.
- High temperature stability: Good high temperature stability, capable of working in environments up to 1200 degrees Celsius, making it suitable for high-temperature, high-power, and high-frequency application scenarios.
- High breakdown field strength: Gallium oxide has a high breakdown field strength, making it widely used in high-voltage equipment.
- Good optical performance: It has good optical transparency in a wide band range from ultraviolet to infrared.
- Good chemical stability: Gallium oxide has high chemical stability at room temperature and pressure, and has good resistance to many acids and bases.
- These characteristics make gallium oxide have broad application potential in fields such as power electronics, optoelectronics, photocatalysis, and gas sensors.