 Dihedral (Shanghai) Science and Technology Co., Ltd
Dihedral (Shanghai) Science and Technology Co., Ltd
- Home
-
Products
-
- Semiconductor crystal
-
Single crystal substrate
-
Multifunctional single crystal substrate
- Barium titanate (BaTiO3)
- Strontium titanate (SrTiO3)
- Iron doped strontium titanate (Fe:SrTiO3)
- Neodymium doped strontium titanate (Nd:SrTiO3)
- Aluminium oxide (Al2O3)
- Potassium tantalum oxide (KTaO3)
- Lead magnesium niobate–lead titanate (PMN-PT)
- Magnesium oxide (MgO)
- Magnesium aluminate spinel (MgAl2O4)
- Lithium aluminate (LiAlO2)
- Lanthanu m aluminate (LaAlO3)
- Lanthanu m strontium aluminate (LaSrAlO4)
- (La,Sr)(Al,Ta)O3
- Neodymium gallate (NdGaO3)
- Terbium gallium garnet (TGG)
- Gadolinium gallium garnet (GGG)
- Sodium chloride (NaCl)
- Potassium bromide (KBr)
- Potassium chloride (KCl)
-
Multifunctional single crystal substrate
-
Functional crystal
- Optical window
- Scintillation crystal
-
Laser crystal
- Rare earth doped lithium yttrium fluoride (RE:LiYF4)
- Rare earth doped lithium lutetium fluoride (RE:LiLuF4)
- Ytterbium doped yttrium aluminium garnet (Yb:YAG)
- Neodymium doped yttrium aluminium garnet (Nd:YAG)
- Erbium doped yttrium aluminium garnet (Er:YAG)
- Holmium doped yttrium aluminium garnet (Ho:YAG)
- Nd,Yb,Er,Tm,Ho,Cr,Lu Infrared laser crystal
- N* crystal
- Metal single crystal
- Material testing analysis
- Material processing
- Scientific research equipment
-
-
Epitaxial Wafer/Films
-
Inorganic epitaxial wafer/film
- Gallium Oxide epitaxial wafer (Ga2O3)
- ε - Gallium Oxide (Ga2O3)
- Platinum/Titanium/Silicon Dioxide/Silicon epitacial wafer (Pt/Ti/SiO2/Si)
- Lithium niobate thin film epitaxial wafer
- Lithium tantalate thin film epitaxial wafer
- InGaAs epitaxial wafer
- Gallium Nitride(GaN) epitaxial wafer
- Epitaxial silicon wafer
- Yttrium Iron Garnet(YIG) epitaxial wafers
- Fullerenes&Fullerols
- ε-Gallium Oxide(Ga2O3)
- Indium Arsenide (InAs) epitaxial wafer
- InGaAs and other compound epitaxial wafers
- Periodic polarization of lithium niobate PPLN and lithium tantalate PPLT
-
Inorganic epitaxial wafer/film
- Functional Glass
- Fine Ceramics
-
2-D material
- 2-D crystal
-
Layered transition metal compound
- Iron chloride (FeCl2)
- Niobium sulfide (NbS3)
- Gallium telluride iodide (GaTeI)
- Indium selenide (InSe)
- Copper indium phosphide sulfide (CuInP2S6)
- Tungsten sulfide selenide (WSSe)
- Iron germanium telluride (Fe3GeTe2)
- Nickel iodide (NiI2)
- Iron phosphorus sulfide (FePS3)
- Manganese phosphorus selenide (MnPSe3)
- Manganese phosphorus sulfide (MnPS3)
- Interface thermal conductive materials
-
Epitaxial Wafer/Films
-
-
High-purity element
- Non-metallic
-
Metal
- Scandium (Sc)
- Titanium (Ti)
- Indium (In)
- Gallium (Ga)
- Bismuth (Bi)
- Tin (Sn)
- Zinc (Zn)
- Cadmium (Cd)
- Antimony (Sb)
- Copper (Cu)
- Nickel (Ni)
- Molybdenum (Mo)
- Aluminium (Al)
- Rhenium (Re)
- Hafnium (Hf)
- Vanadium (V)
- Chromium (Cr)
- Iron (Fe)
- Cobalt (Co)
- Zirconium (Zr)
- Niobium (Nb)
- Tungsten (W)
- Germanium (Ge)
- Iron(Fe)
-
Compound raw materials
-
Oxide
- Tungsten Trioxide (WO3)
- Hafnium Dioxide (HfO2)
- Ytterbium Oxide (Yb2O3)
- Erbium Oxide (Er2O3)
- Lanthanu m Oxide (La2O3)
- Cerium Dioxide (CeO2)
- Tin Dioxide (SnO2)
- Niobium Oxide (Nb2O3)
- Zirconium Dioxide (ZrO2)
- Zinc Oxide (ZnO)
- Copper Oxide (CuO)
- Magnetite (Fe3O4)
- Titanium Dioxide (TiO2)
- Samarium (III) oxide (Sm2O3)
- Silicon Dioxide (SiO2)
- Aluminum Oxide (Al2O3)
- Gallium Oxide Ga2O3(Powder)
- Sulfide
- Fluoride
- Nitride
- Carbide
-
Halide
- Gallium Chloride (GaCl3)
- Indium Chloride (InCl3)
- Aluminum Chloride (AlCl3)
- Bismuth Chloride (BiCl3)
- Cadmium Chloride (CdCl2)
- Chromium Chloride (CrCl2)
- Chromium Chloride Hydrate (CrCl2(H2O)n)
- Copper Chloride (CuCl)
- Copper Chloride II (CuCl2)
- Cesium Chloride (CsCl)
- Europium Chloride (EuCl3)
- Europium Chloride Hydrate (EuCl3.xH2O)
- Magnesium Chloride (MgCl2)
- Sodium Chloride (NaCl)
- Nickel Chloride (NiCl2)
- Indium Chloride (InCl3)
- Indium Nitrate Hydrate (In(NO3).xH2O)
- Rubidium Chloride (RbCl3)
- Antimony Chloride (SbCl3)
- Samarium Chloride (SmCl3)
- Samarium Chloride Hydrate (SmCl3.xH2O)
- Scandium Chloride (ScCl3)
- Tellurium Chloride (TeCl3)
- Tantalum Chloride (TaCl5)
- Tungsten Chloride (WCl6)
- Aluminum Bromide (AlBr3)
- Barium Bromide (BaBr2)
- Cobalt Bromide (CoBr2)
- Cadmium Bromide (CdBr2)
- Gallium Bromide (GaBr3)
- Gallium Bromide Hydrate (GaBr3.xH2O)
- Nickel Bromide (NiBr2)
- Potassium Bromide (KBr)
- Lead Bromide (PbBr2)
- Zirconium Bromide (ZrBr2)
- Bismuth Bromide (BiBr4)
- Bismuth Iodide (BiI3)
- Calcium Iodide (CaI2)
- Gadolinium Iodide (GdI2)
- Cobalt Iodide (CoI2)
- Cesium Iodide (CsI)
- Europium Iodide (EuI2)
- Lithium Iodide (LiI)
- Lithium Iodide Hydrate (LiI.xH2O)
- Gallium Iodide (GaI3)
- Gadolinium Iodide (GdI3)
- Indium Iodide (InI3)
- Potassium Iodide (KI)
- Lanthanu m Iodide (LaI3)
- Lutetium Iodide (LuI3)
- Magnesium Iodide (MgI2)
- Sodium Iodide (NaI)
-
Oxide
-
High-purity element
-
-
Sputtering Target
-
Metal target material
- Gold (Au(T))
- Silver (Ag(T))
- Platinum (Pt(T))
- Palladium (Pd(T))
- Ruthenium (Ru(T))
- Iridium (Ir(T))
- Aluminium (Al(T))
- Copper (Cu(T))
- Titanium (Ti(T))
- Nickel (Ni(T))
- Chromium (Cr(T))
- Cobalt (Co(T))
- Iron (Fe(T))
- Manganese (Mn(T))
- Zinc (Zn(T))
- Vanadium (V(T))
- Tungsten (W(T))
- Hafnium (Hf(T))
- Niobium (Nb(T))
- Molybdenum (Mo(T))
- Lanthanu m (La (T))
- Cerium (Ce (T))
- Praseodymium (Pr (T))
- Neodymium (Nd (T))
- Samarium (Sm (T))
- Europium (Eu (T))
- Gadolinium (Gd (T))
- Terbium (Tb (T))
- Dysprosium (Dy (T))
- Holmium (Ho (T))
- Erbium (Er (T))
- Thulium (Tm (T))
- Ytterbium (Yb (T))
- Lutetium (Lu (T))
- Alloy target material
- Semiconductor target material
-
Oxide target material
- Aluminum Oxide (Al2O3(T))
- Silicon Dioxide (SiO2(T))
- Titanium Dioxide (TiO2(T))
- Chromium Oxide (Cr2O3(T))
- Nickel Oxide (NiO(T))
- Copper Oxide (CuO(T))
- Zinc Oxide (ZnO(T))
- Zirconium Oxide (ZrO2(T))
- Indium Tin Oxide (ITO(T))
- Indium Zinc Oxide (IZO(T))
- Aluminum Doped Zinc Oxide (AZO(T))
- Cerium Oxide (CeO2(T))
- Tungsten Trioxide (WO3(T))
- Hafnium Oxide (HfO2(T))
- Indium Gallium Zinc Oxide (IGZO(T))
- Nitride target material
- Sulfide target material
-
Antimony tellurium selenium boron target material
- Magnesium Boride (MgB2(T))
- Lanthanu m Hexaboride (LaB6(T))
- Titanium Diboride (TiB2(T))
- Zinc Selenide (ZnSe(T))
- Zinc Antimonide (Zn4Sb3(T))
- Cadmium Selenide (CdSe(T))
- Indium Telluride (In2Te3(T))
- Tin Selenide (SnSe(T))
- Germanium Antimonide (GeSb(T))
- Antimony Selenide (Sb2Se3(T))
- Antimony Telluride (Sb2Te3(T))
- Bismuth Telluride (Bi2Te3(T))
-
Metal target material
-
Sputtering Target
-
- Services
- Media
- Partner
- Contact Us
- About
- Home
- Products
- Semiconductor crystal
- Compound semiconductor
- Semiconductor crystal
-
Functional crystal
- Optical window
- Scintillation crystal
-
Laser crystal
- Rare earth doped lithium yttrium fluoride (RE:LiYF4)
- Rare earth doped lithium lutetium fluoride (RE:LiLuF4)
- Ytterbium doped yttrium aluminium garnet (Yb:YAG)
- Neodymium doped yttrium aluminium garnet (Nd:YAG)
- Erbium doped yttrium aluminium garnet (Er:YAG)
- Holmium doped yttrium aluminium garnet (Ho:YAG)
- Nd,Yb,Er,Tm,Ho,Cr,Lu Infrared laser crystal
- N* crystal
- Metal single crystal
-
2-D material
- 2-D crystal
-
Layered transition metal compound
- Iron chloride (FeCl2)
- Niobium sulfide (NbS3)
- Gallium telluride iodide (GaTeI)
- Indium selenide (InSe)
- Copper indium phosphide sulfide (CuInP2S6)
- Tungsten sulfide selenide (WSSe)
- Iron germanium telluride (Fe3GeTe2)
- Nickel iodide (NiI2)
- Iron phosphorus sulfide (FePS3)
- Manganese phosphorus selenide (MnPSe3)
- Manganese phosphorus sulfide (MnPS3)
-
High-purity element
- Non-metallic
-
Metal
- Scandium (Sc)
- Titanium (Ti)
- Indium (In)
- Gallium (Ga)
- Bismuth (Bi)
- Tin (Sn)
- Zinc (Zn)
- Cadmium (Cd)
- Antimony (Sb)
- Copper (Cu)
- Nickel (Ni)
- Molybdenum (Mo)
- Aluminium (Al)
- Rhenium (Re)
- Hafnium (Hf)
- Vanadium (V)
- Chromium (Cr)
- Iron (Fe)
- Cobalt (Co)
- Zirconium (Zr)
- Niobium (Nb)
- Tungsten (W)
- Germanium (Ge)
- Iron(Fe)
-
Single crystal substrate
-
Multifunctional single crystal substrate
- Barium titanate (BaTiO3)
- Strontium titanate (SrTiO3)
- Iron doped strontium titanate (Fe:SrTiO3)
- Neodymium doped strontium titanate (Nd:SrTiO3)
- Aluminium oxide (Al2O3)
- Potassium tantalum oxide (KTaO3)
- Lead magnesium niobate–lead titanate (PMN-PT)
- Magnesium oxide (MgO)
- Magnesium aluminate spinel (MgAl2O4)
- Lithium aluminate (LiAlO2)
- Lanthanu m aluminate (LaAlO3)
- Lanthanu m strontium aluminate (LaSrAlO4)
- (La,Sr)(Al,Ta)O3
- Neodymium gallate (NdGaO3)
- Terbium gallium garnet (TGG)
- Gadolinium gallium garnet (GGG)
- Sodium chloride (NaCl)
- Potassium bromide (KBr)
- Potassium chloride (KCl)
-
Multifunctional single crystal substrate
-
Sputtering Target
-
Metal target material
- Gold (Au(T))
- Silver (Ag(T))
- Platinum (Pt(T))
- Palladium (Pd(T))
- Ruthenium (Ru(T))
- Iridium (Ir(T))
- Aluminium (Al(T))
- Copper (Cu(T))
- Titanium (Ti(T))
- Nickel (Ni(T))
- Chromium (Cr(T))
- Cobalt (Co(T))
- Iron (Fe(T))
- Manganese (Mn(T))
- Zinc (Zn(T))
- Vanadium (V(T))
- Tungsten (W(T))
- Hafnium (Hf(T))
- Niobium (Nb(T))
- Molybdenum (Mo(T))
- Lanthanu m (La (T))
- Cerium (Ce (T))
- Praseodymium (Pr (T))
- Neodymium (Nd (T))
- Samarium (Sm (T))
- Europium (Eu (T))
- Gadolinium (Gd (T))
- Terbium (Tb (T))
- Dysprosium (Dy (T))
- Holmium (Ho (T))
- Erbium (Er (T))
- Thulium (Tm (T))
- Ytterbium (Yb (T))
- Lutetium (Lu (T))
- Alloy target material
- Semiconductor target material
-
Oxide target material
- Aluminum Oxide (Al2O3(T))
- Silicon Dioxide (SiO2(T))
- Titanium Dioxide (TiO2(T))
- Chromium Oxide (Cr2O3(T))
- Nickel Oxide (NiO(T))
- Copper Oxide (CuO(T))
- Zinc Oxide (ZnO(T))
- Zirconium Oxide (ZrO2(T))
- Indium Tin Oxide (ITO(T))
- Indium Zinc Oxide (IZO(T))
- Aluminum Doped Zinc Oxide (AZO(T))
- Cerium Oxide (CeO2(T))
- Tungsten Trioxide (WO3(T))
- Hafnium Oxide (HfO2(T))
- Indium Gallium Zinc Oxide (IGZO(T))
- Nitride target material
- Sulfide target material
-
Antimony tellurium selenium boron target material
- Magnesium Boride (MgB2(T))
- Lanthanu m Hexaboride (LaB6(T))
- Titanium Diboride (TiB2(T))
- Zinc Selenide (ZnSe(T))
- Zinc Antimonide (Zn4Sb3(T))
- Cadmium Selenide (CdSe(T))
- Indium Telluride (In2Te3(T))
- Tin Selenide (SnSe(T))
- Germanium Antimonide (GeSb(T))
- Antimony Selenide (Sb2Se3(T))
- Antimony Telluride (Sb2Te3(T))
- Bismuth Telluride (Bi2Te3(T))
-
Metal target material
- Interface thermal conductive materials
-
Compound raw materials
-
Oxide
- Tungsten Trioxide (WO3)
- Hafnium Dioxide (HfO2)
- Ytterbium Oxide (Yb2O3)
- Erbium Oxide (Er2O3)
- Lanthanu m Oxide (La2O3)
- Cerium Dioxide (CeO2)
- Tin Dioxide (SnO2)
- Niobium Oxide (Nb2O3)
- Zirconium Dioxide (ZrO2)
- Zinc Oxide (ZnO)
- Copper Oxide (CuO)
- Magnetite (Fe3O4)
- Titanium Dioxide (TiO2)
- Samarium (III) oxide (Sm2O3)
- Silicon Dioxide (SiO2)
- Aluminum Oxide (Al2O3)
- Gallium Oxide Ga2O3(Powder)
- Sulfide
- Fluoride
- Nitride
- Carbide
-
Halide
- Gallium Chloride (GaCl3)
- Indium Chloride (InCl3)
- Aluminum Chloride (AlCl3)
- Bismuth Chloride (BiCl3)
- Cadmium Chloride (CdCl2)
- Chromium Chloride (CrCl2)
- Chromium Chloride Hydrate (CrCl2(H2O)n)
- Copper Chloride (CuCl)
- Copper Chloride II (CuCl2)
- Cesium Chloride (CsCl)
- Europium Chloride (EuCl3)
- Europium Chloride Hydrate (EuCl3.xH2O)
- Magnesium Chloride (MgCl2)
- Sodium Chloride (NaCl)
- Nickel Chloride (NiCl2)
- Indium Chloride (InCl3)
- Indium Nitrate Hydrate (In(NO3).xH2O)
- Rubidium Chloride (RbCl3)
- Antimony Chloride (SbCl3)
- Samarium Chloride (SmCl3)
- Samarium Chloride Hydrate (SmCl3.xH2O)
- Scandium Chloride (ScCl3)
- Tellurium Chloride (TeCl3)
- Tantalum Chloride (TaCl5)
- Tungsten Chloride (WCl6)
- Aluminum Bromide (AlBr3)
- Barium Bromide (BaBr2)
- Cobalt Bromide (CoBr2)
- Cadmium Bromide (CdBr2)
- Gallium Bromide (GaBr3)
- Gallium Bromide Hydrate (GaBr3.xH2O)
- Nickel Bromide (NiBr2)
- Potassium Bromide (KBr)
- Lead Bromide (PbBr2)
- Zirconium Bromide (ZrBr2)
- Bismuth Bromide (BiBr4)
- Bismuth Iodide (BiI3)
- Calcium Iodide (CaI2)
- Gadolinium Iodide (GdI2)
- Cobalt Iodide (CoI2)
- Cesium Iodide (CsI)
- Europium Iodide (EuI2)
- Lithium Iodide (LiI)
- Lithium Iodide Hydrate (LiI.xH2O)
- Gallium Iodide (GaI3)
- Gadolinium Iodide (GdI3)
- Indium Iodide (InI3)
- Potassium Iodide (KI)
- Lanthanu m Iodide (LaI3)
- Lutetium Iodide (LuI3)
- Magnesium Iodide (MgI2)
- Sodium Iodide (NaI)
-
Oxide
-
Epitaxial Wafer/Films
-
Inorganic epitaxial wafer/film
- Gallium Oxide epitaxial wafer (Ga2O3)
- ε - Gallium Oxide (Ga2O3)
- Platinum/Titanium/Silicon Dioxide/Silicon epitacial wafer (Pt/Ti/SiO2/Si)
- Lithium niobate thin film epitaxial wafer
- Lithium tantalate thin film epitaxial wafer
- InGaAs epitaxial wafer
- Gallium Nitride(GaN) epitaxial wafer
- Epitaxial silicon wafer
- Yttrium Iron Garnet(YIG) epitaxial wafers
- Fullerenes&Fullerols
- ε-Gallium Oxide(Ga2O3)
- Indium Arsenide (InAs) epitaxial wafer
- InGaAs and other compound epitaxial wafers
- Periodic polarization of lithium niobate PPLN and lithium tantalate PPLT
-
Inorganic epitaxial wafer/film
- Material testing analysis
- Scientific research equipment
- Material processing
- Functional Glass
- Fine Ceramics
Compound semiconductor
Gallium oxide (Ga2O3)
Gallium oxide (Ga2O3) is a semiconductor material with good chemical and thermal stability. Its bandgap width is 4.7-4.9 eV, critical breakdown field strength is 8 MV/cm (much higher than the theoretical limit of 2.5 MV/cm for SiC and 3.3 MV/cm for GaN), electron mobility is 250 cm2/V • s, and it has strong transparent conductivity. The Barigard value exceeds 3000, which is several times that of GaN and SiC materials.
Gallium nitride (GaN)

Gallium nitride (GaN) is a wide bandgap semiconductor material with excellent properties such as high electron mobility, high thermal conductivity and high radiation resistance. GaN is widely used in LED lamp manufacturing, RF applications, power electronics and solar cells. Especially in the field of power electronics, GaN is regarded as an important material for future power systems because it can withstand higher voltages and temperatures. At the same time, the radiation resistance properties
Silicon carbide (SiC)

Silicon carbide SiC crystal is a wide bandgap semiconductor material with excellent thermal conductivity and high electric field breakdown strength, which makes it have significant performance advantages in harsh environments such as high power, high frequency and high temperature. SiC crystals are widely used in power electronic equipment, such as power devices in electric vehicles, rail transit, power grids and other fields, and can also be used as materials for high-temperature, high-frequenc
Gallium arsenide (GaAs)

GaAs crystal is a direct bandgap semiconductor material with good electron migration performance and high electron velocity, which is suitable for high-speed electronic devices. Compared to silicon, GaAs is better suited to manufacturing faster electronics. In addition, GaAs crystals have a strong absorption capacity for light, so they are widely used in optoelectronic fields such as solar cells, photodiodes, and laser diodes.
Indium phosphide (InP)
Indium phosphide (InP) is an important III-V semiconductor material with direct bandgap properties and high electron mobility. InP single crystal has a band gap of about 1.35 eV and excellent optical and electronic properties at room temperature. InP is often used to make high-speed electronic devices, including high-frequency, high-speed optical fiber communication systems, microwave devices, and some high-efficiency solar cells. In addition, due to the high refractive index and good thermal st
Gallium antimonide (GaSb)
GaSb is the chemical formula of gallium arsenide, an important semiconductor material. It has a wide range of applications, including infrared detectors, lasers, photoelectric sensors, etc. GaSb's outstanding properties include high electron mobility, wide bandgap, low noise, and high saturation drift speed, making it ideal for infrared technology and optoelectronics.
Indium arsenide (InAs)
InAs is the chemical formula of indium arsenide, an important semiconductor material. It has excellent electronic motion performance and optical characteristics, and is widely used in infrared detectors, photoelectric sensors, lasers and other fields. InAs offers high carrier mobility, wide bandgap adjustment range, and fast response speed, providing good performance for infrared optics and electronics.
Zinc oxide (ZnO)

ZnO is the chemical formula of zinc oxide and is a widely used semiconductor material. It has excellent optoelectronic properties and optical properties and can be used in optoelectronic devices, optical coatings, sensors, etc. The advantages of ZnO include wide bandgap, high transparency, excellent electron transport performance and good chemical stability, making it an important application value in optoelectronics and optics.
Cadmium zinc telluride (CdZnTe)
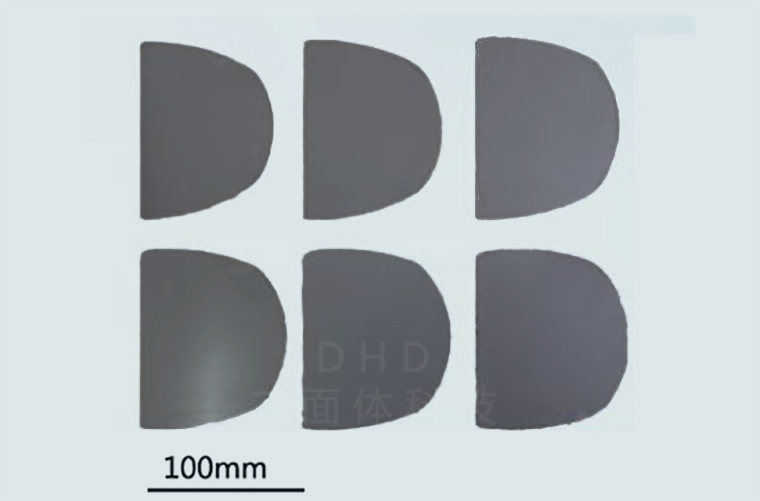
CdZnTe is the chemical formula of zinc cadmium telluride, which is an important semiconductor material. It has wide bandgap and high electron mobility and is widely used in X-ray and γ-ray detectors, nuclear medicine imaging, and other fields. The advantages of CdZnTe include high energy resolution, fast response time, and good radiation hardness, making it a key material for radiographic detection and imaging techniques.
Aluminum Nitride (AlN) crystal/substrate/film
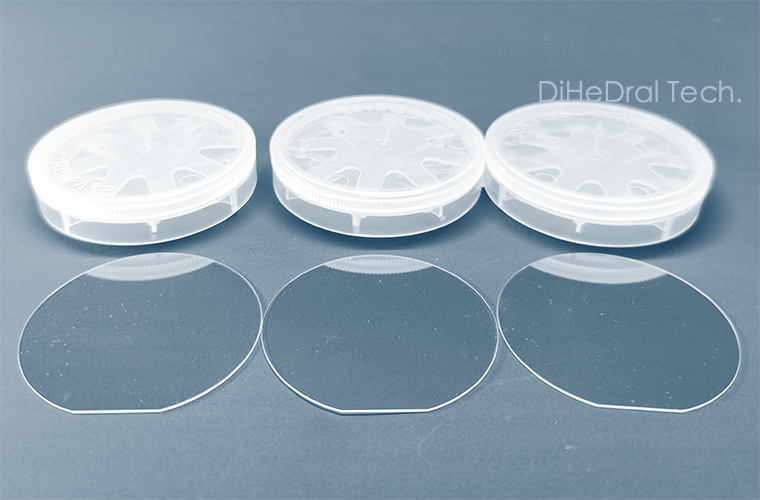
Aluminum nitride (AlN), with a wide band gap (6.2eV), ultra-high breakdown voltage, and perfect lattice match with high aluminum content AlGaN epitaxial layer, can be widely used in deep ultraviolet detectors, semiconductor laser, and high power microwave devices.

