 Dihedral (Shanghai) Science and Technology Co., Ltd
Dihedral (Shanghai) Science and Technology Co., Ltd
- Home
-
Products
-
- Semiconductor crystal
-
Single crystal substrate
-
Multifunctional single crystal substrate
- Barium titanate (BaTiO3)
- Strontium titanate (SrTiO3)
- Iron doped strontium titanate (Fe:SrTiO3)
- Neodymium doped strontium titanate (Nd:SrTiO3)
- Aluminium oxide (Al2O3)
- Potassium tantalum oxide (KTaO3)
- Lead magnesium niobate–lead titanate (PMN-PT)
- Magnesium oxide (MgO)
- Magnesium aluminate spinel (MgAl2O4)
- Lithium aluminate (LiAlO2)
- Lanthanu m aluminate (LaAlO3)
- Lanthanu m strontium aluminate (LaSrAlO4)
- (La,Sr)(Al,Ta)O3
- Neodymium gallate (NdGaO3)
- Terbium gallium garnet (TGG)
- Gadolinium gallium garnet (GGG)
- Sodium chloride (NaCl)
- Potassium bromide (KBr)
- Potassium chloride (KCl)
-
Multifunctional single crystal substrate
-
Functional crystal
- Optical window
- Scintillation crystal
-
Laser crystal
- Rare earth doped lithium yttrium fluoride (RE:LiYF4)
- Rare earth doped lithium lutetium fluoride (RE:LiLuF4)
- Ytterbium doped yttrium aluminium garnet (Yb:YAG)
- Neodymium doped yttrium aluminium garnet (Nd:YAG)
- Erbium doped yttrium aluminium garnet (Er:YAG)
- Holmium doped yttrium aluminium garnet (Ho:YAG)
- Nd,Yb,Er,Tm,Ho,Cr,Lu Infrared laser crystal
- N* crystal
- Metal single crystal
- Material testing analysis
- Material processing
- Scientific research equipment
-
-
Epitaxial Wafer/Films
-
Inorganic epitaxial wafer/film
- Gallium Oxide epitaxial wafer (Ga2O3)
- ε - Gallium Oxide (Ga2O3)
- Platinum/Titanium/Silicon Dioxide/Silicon epitacial wafer (Pt/Ti/SiO2/Si)
- Lithium niobate thin film epitaxial wafer
- Lithium tantalate thin film epitaxial wafer
- InGaAs epitaxial wafer
- Gallium Nitride(GaN) epitaxial wafer
- Epitaxial silicon wafer
- Yttrium Iron Garnet(YIG) epitaxial wafers
- Fullerenes&Fullerols
-
Inorganic epitaxial wafer/film
- Functional Glass
- Fine Ceramics
-
2-D material
- 2-D crystal
-
Layered transition metal compound
- Iron chloride (FeCl2)
- Niobium sulfide (NbS3)
- Gallium telluride iodide (GaTeI)
- Indium selenide (InSe)
- Copper indium phosphide sulfide (CuInP2S6)
- Tungsten sulfide selenide (WSSe)
- Iron germanium telluride (Fe3GeTe2)
- Nickel iodide (NiI2)
- Iron phosphorus sulfide (FePS3)
- Manganese phosphorus selenide (MnPSe3)
- Manganese phosphorus sulfide (MnPS3)
- Interface thermal conductive materials
-
Epitaxial Wafer/Films
-
-
High-purity element
- Non-metallic
-
Metal
- Scandium (Sc)
- Titanium (Ti)
- Indium (In)
- Gallium (Ga)
- Bismuth (Bi)
- Tin (Sn)
- Zinc (Zn)
- Cadmium (Cd)
- Antimony (Sb)
- Copper (Cu)
- Nickel (Ni)
- Molybdenum (Mo)
- Aluminium (Al)
- Rhenium (Re)
- Hafnium (Hf)
- Vanadium (V)
- Chromium (Cr)
- Iron (Fe)
- Cobalt (Co)
- Zirconium (Zr)
- Niobium (Nb)
- Tungsten (W)
- Germanium (Ge)
- Iron(Fe)
-
Compound raw materials
-
Oxide
- Tungsten Trioxide (WO3)
- Hafnium Dioxide (HfO2)
- Ytterbium Oxide (Yb2O3)
- Erbium Oxide (Er2O3)
- Lanthanu m Oxide (La2O3)
- Cerium Dioxide (CeO2)
- Tin Dioxide (SnO2)
- Niobium Oxide (Nb2O3)
- Zirconium Dioxide (ZrO2)
- Zinc Oxide (ZnO)
- Copper Oxide (CuO)
- Magnetite (Fe3O4)
- Titanium Dioxide (TiO2)
- Samarium (III) oxide (Sm2O3)
- Silicon Dioxide (SiO2)
- Aluminum Oxide (Al2O3)
- Gallium Oxide Ga2O3(Powder)
- Sulfide
- Fluoride
- Nitride
- Carbide
-
Halide
- Gallium Chloride (GaCl3)
- Indium Chloride (InCl3)
- Aluminum Chloride (AlCl3)
- Bismuth Chloride (BiCl3)
- Cadmium Chloride (CdCl2)
- Chromium Chloride (CrCl2)
- Chromium Chloride Hydrate (CrCl2(H2O)n)
- Copper Chloride (CuCl)
- Copper Chloride II (CuCl2)
- Cesium Chloride (CsCl)
- Europium Chloride (EuCl3)
- Europium Chloride Hydrate (EuCl3.xH2O)
- Magnesium Chloride (MgCl2)
- Sodium Chloride (NaCl)
- Nickel Chloride (NiCl2)
- Indium Chloride (InCl3)
- Indium Nitrate Hydrate (In(NO3).xH2O)
- Rubidium Chloride (RbCl3)
- Antimony Chloride (SbCl3)
- Samarium Chloride (SmCl3)
- Samarium Chloride Hydrate (SmCl3.xH2O)
- Scandium Chloride (ScCl3)
- Tellurium Chloride (TeCl3)
- Tantalum Chloride (TaCl5)
- Tungsten Chloride (WCl6)
- Aluminum Bromide (AlBr3)
- Barium Bromide (BaBr2)
- Cobalt Bromide (CoBr2)
- Cadmium Bromide (CdBr2)
- Gallium Bromide (GaBr3)
- Gallium Bromide Hydrate (GaBr3.xH2O)
- Nickel Bromide (NiBr2)
- Potassium Bromide (KBr)
- Lead Bromide (PbBr2)
- Zirconium Bromide (ZrBr2)
- Bismuth Bromide (BiBr4)
- Bismuth Iodide (BiI3)
- Calcium Iodide (CaI2)
- Gadolinium Iodide (GdI2)
- Cobalt Iodide (CoI2)
- Cesium Iodide (CsI)
- Europium Iodide (EuI2)
- Lithium Iodide (LiI)
- Lithium Iodide Hydrate (LiI.xH2O)
- Gallium Iodide (GaI3)
- Gadolinium Iodide (GdI3)
- Indium Iodide (InI3)
- Potassium Iodide (KI)
- Lanthanu m Iodide (LaI3)
- Lutetium Iodide (LuI3)
- Magnesium Iodide (MgI2)
- Sodium Iodide (NaI)
-
Oxide
-
High-purity element
-
-
Sputtering Target
-
Metal target material
- Gold (Au(T))
- Silver (Ag(T))
- Platinum (Pt(T))
- Palladium (Pd(T))
- Ruthenium (Ru(T))
- Iridium (Ir(T))
- Aluminium (Al(T))
- Copper (Cu(T))
- Titanium (Ti(T))
- Nickel (Ni(T))
- Chromium (Cr(T))
- Cobalt (Co(T))
- Iron (Fe(T))
- Manganese (Mn(T))
- Zinc (Zn(T))
- Vanadium (V(T))
- Tungsten (W(T))
- Hafnium (Hf(T))
- Niobium (Nb(T))
- Molybdenum (Mo(T))
- Lanthanu m (La (T))
- Cerium (Ce (T))
- Praseodymium (Pr (T))
- Neodymium (Nd (T))
- Samarium (Sm (T))
- Europium (Eu (T))
- Gadolinium (Gd (T))
- Terbium (Tb (T))
- Dysprosium (Dy (T))
- Holmium (Ho (T))
- Erbium (Er (T))
- Thulium (Tm (T))
- Ytterbium (Yb (T))
- Lutetium (Lu (T))
- Alloy target material
- Semiconductor target material
-
Oxide target material
- Aluminum Oxide (Al2O3(T))
- Silicon Dioxide (SiO2(T))
- Titanium Dioxide (TiO2(T))
- Chromium Oxide (Cr2O3(T))
- Nickel Oxide (NiO(T))
- Copper Oxide (CuO(T))
- Zinc Oxide (ZnO(T))
- Zirconium Oxide (ZrO2(T))
- Indium Tin Oxide (ITO(T))
- Indium Zinc Oxide (IZO(T))
- Aluminum Doped Zinc Oxide (AZO(T))
- Cerium Oxide (CeO2(T))
- Tungsten Trioxide (WO3(T))
- Hafnium Oxide (HfO2(T))
- Indium Gallium Zinc Oxide (IGZO(T))
- Nitride target material
- Sulfide target material
-
Antimony tellurium selenium boron target material
- Magnesium Boride (MgB2(T))
- Lanthanu m Hexaboride (LaB6(T))
- Titanium Diboride (TiB2(T))
- Zinc Selenide (ZnSe(T))
- Zinc Antimonide (Zn4Sb3(T))
- Cadmium Selenide (CdSe(T))
- Indium Telluride (In2Te3(T))
- Tin Selenide (SnSe(T))
- Germanium Antimonide (GeSb(T))
- Antimony Selenide (Sb2Se3(T))
- Antimony Telluride (Sb2Te3(T))
- Bismuth Telluride (Bi2Te3(T))
-
Metal target material
-
Sputtering Target
-
- Services
- Media
- Partner
- Contact Us
- About
- Home
- Products
- Epitaxial Wafer/Films
- Inorganic epitaxial wafer/film
- Epitaxial silicon wafer
Epitaxial silicon wafer
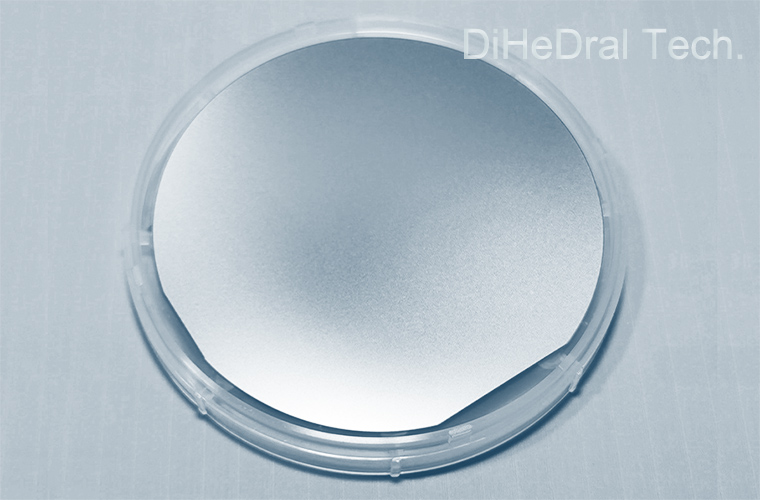
Silicon epitaxial wafers are commonly used in the field of semiconductor manufacturing, especially in integrated circuit manufacturing. Through epitaxial technology, different silicon layers can be achieved on the same silicon wafer, each with different electrical characteristics. This helps to integrate devices with different functions on the same chip, improving integration and performance.
Applications
Silicon epitaxial wafers have various applications in the semiconductor industry, mainly related to integrated circuit manufacturing and optoelectronic devices. The following are the main application areas of silicon epitaxial wafers:
1. Integrated circuit manufacturing: Silicon epitaxial wafers are widely used in the manufacturing of integrated circuits. By epitaxial different layers of silicon on the same silicon wafer, manufacturers can create complex semiconductor devices and integrated circuits. This helps to improve the integration, performance, and power efficiency of the chip.
2. Optoelectronic devices: Silicon epitaxial wafers are also used to manufacture optoelectronic devices, such as photodiodes, photovoltaic cells, and lasers. In these applications, silicon epitaxial wafers provide high-quality, high crystal purity silicon materials, which help improve the performance and stability of devices.
3. Sensor manufacturing: Some sensors, especially those related to semiconductor technology, may also be manufactured using silicon epitaxial wafers. These sensors can be used to measure physical quantities such as temperature, pressure, and light intensity.
4. Microelectronics research: In the research and development of new microelectronics devices and technologies, silicon epitaxial wafers are an important experimental tool. Researchers can use epitaxial processes to explore new semiconductor materials, structures, and device designs.
5. Infrared detectors: Some infrared detectors are manufactured using silicon epitaxial wafers for high sensitivity detection within the infrared spectral range.
Overall, the application of silicon epitaxial wafers in the fields of semiconductors and optoelectronics provides key support for the manufacturing and performance of modern electronic devices, promoting continuous technological progress.
Features
Basic silicon wafer substrate: Select a basic silicon wafer as the substrate. This silicon wafer typically has the required lattice structure and orientation to support subsequent silicon epitaxial growth.
Epitaxy process: Epitaxy is a technique used to deposit new crystal layers on the surface of a crystal. In the preparation of silicon epitaxial wafers, a new layer of silicon single crystal is grown by depositing silicon material on the base silicon wafer.
Growth temperature and atmosphere control: During the epitaxial process, it is necessary to control the temperature and atmosphere to ensure that the newly grown silicon layer has the required crystal quality and structure. This is to avoid crystal defects and ensure the quality and performance of silicon wafers.
Doping and other treatments: During the preparation process of silicon epitaxial wafers, the electrical properties of the silicon wafer can be adjusted through doping and other treatments. This is to give silicon wafers specific electrical properties to meet the needs of specific applications.
-
Epitaxial layer doping
Parameters
Si-Si epitaxial wafer
Sapphire substrate silicon epitaxial wafer
Diameter
76, 100, 150, 200 mm
76, 100, 150 mm
Substrate crystal orientation
(111), (100)
R-face
Substrate doping
Antimony, Boron, Arsenic
-
Thickness(μm)
1,0 – 200
0,3 – 2,0
Phosphorus, Boron, Arsenic
Phosphorus, Boron
Epitaxial layer resistivity, Ω.cm
N-type2
P-type1
0,005 – 1500
0,005 – 1500
acc. to spec.
1,0 - 0,01
Multilayer output
To the fourth layer
1 layer
Buried epitaxy
To the third layer
(p+, n+)
-

