 Dihedral (Shanghai) Science and Technology Co., Ltd
Dihedral (Shanghai) Science and Technology Co., Ltd
- Home
-
Products
-
- Semiconductor crystal
-
Single crystal substrate
-
Multifunctional single crystal substrate
- Barium titanate (BaTiO3)
- Strontium titanate (SrTiO3)
- Iron doped strontium titanate (Fe:SrTiO3)
- Neodymium doped strontium titanate (Nd:SrTiO3)
- Aluminium oxide (Al2O3)
- Potassium tantalum oxide (KTaO3)
- Lead magnesium niobate–lead titanate (PMN-PT)
- Magnesium oxide (MgO)
- Magnesium aluminate spinel (MgAl2O4)
- Lithium aluminate (LiAlO2)
- Lanthanu m aluminate (LaAlO3)
- Lanthanu m strontium aluminate (LaSrAlO4)
- (La,Sr)(Al,Ta)O3
- Neodymium gallate (NdGaO3)
- Terbium gallium garnet (TGG)
- Gadolinium gallium garnet (GGG)
- Sodium chloride (NaCl)
- Potassium bromide (KBr)
- Potassium chloride (KCl)
-
Multifunctional single crystal substrate
-
Functional crystal
- Optical window
- Scintillation crystal
-
Laser crystal
- Rare earth doped lithium yttrium fluoride (RE:LiYF4)
- Rare earth doped lithium lutetium fluoride (RE:LiLuF4)
- Ytterbium doped yttrium aluminium garnet (Yb:YAG)
- Neodymium doped yttrium aluminium garnet (Nd:YAG)
- Erbium doped yttrium aluminium garnet (Er:YAG)
- Holmium doped yttrium aluminium garnet (Ho:YAG)
- Nd,Yb,Er,Tm,Ho,Cr,Lu Infrared laser crystal
- N* crystal
- Metal single crystal
- Material testing analysis
- Material processing
- Scientific research equipment
-
-
Epitaxial Wafer/Films
-
Inorganic epitaxial wafer/film
- Gallium Oxide epitaxial wafer (Ga2O3)
- ε - Gallium Oxide (Ga2O3)
- Platinum/Titanium/Silicon Dioxide/Silicon epitacial wafer (Pt/Ti/SiO2/Si)
- Lithium niobate thin film epitaxial wafer
- Lithium tantalate thin film epitaxial wafer
- InGaAs epitaxial wafer
- Gallium Nitride(GaN) epitaxial wafer
- Epitaxial silicon wafer
- Yttrium Iron Garnet(YIG) epitaxial wafers
- Fullerenes&Fullerols
-
Inorganic epitaxial wafer/film
- Functional Glass
- Fine Ceramics
-
2-D material
- 2-D crystal
-
Layered transition metal compound
- Iron chloride (FeCl2)
- Niobium sulfide (NbS3)
- Gallium telluride iodide (GaTeI)
- Indium selenide (InSe)
- Copper indium phosphide sulfide (CuInP2S6)
- Tungsten sulfide selenide (WSSe)
- Iron germanium telluride (Fe3GeTe2)
- Nickel iodide (NiI2)
- Iron phosphorus sulfide (FePS3)
- Manganese phosphorus selenide (MnPSe3)
- Manganese phosphorus sulfide (MnPS3)
- Interface thermal conductive materials
-
Epitaxial Wafer/Films
-
-
High-purity element
- Non-metallic
-
Metal
- Scandium (Sc)
- Titanium (Ti)
- Indium (In)
- Gallium (Ga)
- Bismuth (Bi)
- Tin (Sn)
- Zinc (Zn)
- Cadmium (Cd)
- Antimony (Sb)
- Copper (Cu)
- Nickel (Ni)
- Molybdenum (Mo)
- Aluminium (Al)
- Rhenium (Re)
- Hafnium (Hf)
- Vanadium (V)
- Chromium (Cr)
- Iron (Fe)
- Cobalt (Co)
- Zirconium (Zr)
- Niobium (Nb)
- Tungsten (W)
- Germanium (Ge)
- Iron(Fe)
-
Compound raw materials
-
Oxide
- Tungsten Trioxide (WO3)
- Hafnium Dioxide (HfO2)
- Ytterbium Oxide (Yb2O3)
- Erbium Oxide (Er2O3)
- Lanthanu m Oxide (La2O3)
- Cerium Dioxide (CeO2)
- Tin Dioxide (SnO2)
- Niobium Oxide (Nb2O3)
- Zirconium Dioxide (ZrO2)
- Zinc Oxide (ZnO)
- Copper Oxide (CuO)
- Magnetite (Fe3O4)
- Titanium Dioxide (TiO2)
- Samarium (III) oxide (Sm2O3)
- Silicon Dioxide (SiO2)
- Aluminum Oxide (Al2O3)
- Gallium Oxide Ga2O3(Powder)
- Sulfide
- Fluoride
- Nitride
- Carbide
-
Halide
- Gallium Chloride (GaCl3)
- Indium Chloride (InCl3)
- Aluminum Chloride (AlCl3)
- Bismuth Chloride (BiCl3)
- Cadmium Chloride (CdCl2)
- Chromium Chloride (CrCl2)
- Chromium Chloride Hydrate (CrCl2(H2O)n)
- Copper Chloride (CuCl)
- Copper Chloride II (CuCl2)
- Cesium Chloride (CsCl)
- Europium Chloride (EuCl3)
- Europium Chloride Hydrate (EuCl3.xH2O)
- Magnesium Chloride (MgCl2)
- Sodium Chloride (NaCl)
- Nickel Chloride (NiCl2)
- Indium Chloride (InCl3)
- Indium Nitrate Hydrate (In(NO3).xH2O)
- Rubidium Chloride (RbCl3)
- Antimony Chloride (SbCl3)
- Samarium Chloride (SmCl3)
- Samarium Chloride Hydrate (SmCl3.xH2O)
- Scandium Chloride (ScCl3)
- Tellurium Chloride (TeCl3)
- Tantalum Chloride (TaCl5)
- Tungsten Chloride (WCl6)
- Aluminum Bromide (AlBr3)
- Barium Bromide (BaBr2)
- Cobalt Bromide (CoBr2)
- Cadmium Bromide (CdBr2)
- Gallium Bromide (GaBr3)
- Gallium Bromide Hydrate (GaBr3.xH2O)
- Nickel Bromide (NiBr2)
- Potassium Bromide (KBr)
- Lead Bromide (PbBr2)
- Zirconium Bromide (ZrBr2)
- Bismuth Bromide (BiBr4)
- Bismuth Iodide (BiI3)
- Calcium Iodide (CaI2)
- Gadolinium Iodide (GdI2)
- Cobalt Iodide (CoI2)
- Cesium Iodide (CsI)
- Europium Iodide (EuI2)
- Lithium Iodide (LiI)
- Lithium Iodide Hydrate (LiI.xH2O)
- Gallium Iodide (GaI3)
- Gadolinium Iodide (GdI3)
- Indium Iodide (InI3)
- Potassium Iodide (KI)
- Lanthanu m Iodide (LaI3)
- Lutetium Iodide (LuI3)
- Magnesium Iodide (MgI2)
- Sodium Iodide (NaI)
-
Oxide
-
High-purity element
-
-
Sputtering Target
-
Metal target material
- Gold (Au(T))
- Silver (Ag(T))
- Platinum (Pt(T))
- Palladium (Pd(T))
- Ruthenium (Ru(T))
- Iridium (Ir(T))
- Aluminium (Al(T))
- Copper (Cu(T))
- Titanium (Ti(T))
- Nickel (Ni(T))
- Chromium (Cr(T))
- Cobalt (Co(T))
- Iron (Fe(T))
- Manganese (Mn(T))
- Zinc (Zn(T))
- Vanadium (V(T))
- Tungsten (W(T))
- Hafnium (Hf(T))
- Niobium (Nb(T))
- Molybdenum (Mo(T))
- Lanthanu m (La (T))
- Cerium (Ce (T))
- Praseodymium (Pr (T))
- Neodymium (Nd (T))
- Samarium (Sm (T))
- Europium (Eu (T))
- Gadolinium (Gd (T))
- Terbium (Tb (T))
- Dysprosium (Dy (T))
- Holmium (Ho (T))
- Erbium (Er (T))
- Thulium (Tm (T))
- Ytterbium (Yb (T))
- Lutetium (Lu (T))
- Alloy target material
- Semiconductor target material
-
Oxide target material
- Aluminum Oxide (Al2O3(T))
- Silicon Dioxide (SiO2(T))
- Titanium Dioxide (TiO2(T))
- Chromium Oxide (Cr2O3(T))
- Nickel Oxide (NiO(T))
- Copper Oxide (CuO(T))
- Zinc Oxide (ZnO(T))
- Zirconium Oxide (ZrO2(T))
- Indium Tin Oxide (ITO(T))
- Indium Zinc Oxide (IZO(T))
- Aluminum Doped Zinc Oxide (AZO(T))
- Cerium Oxide (CeO2(T))
- Tungsten Trioxide (WO3(T))
- Hafnium Oxide (HfO2(T))
- Indium Gallium Zinc Oxide (IGZO(T))
- Nitride target material
- Sulfide target material
-
Antimony tellurium selenium boron target material
- Magnesium Boride (MgB2(T))
- Lanthanu m Hexaboride (LaB6(T))
- Titanium Diboride (TiB2(T))
- Zinc Selenide (ZnSe(T))
- Zinc Antimonide (Zn4Sb3(T))
- Cadmium Selenide (CdSe(T))
- Indium Telluride (In2Te3(T))
- Tin Selenide (SnSe(T))
- Germanium Antimonide (GeSb(T))
- Antimony Selenide (Sb2Se3(T))
- Antimony Telluride (Sb2Te3(T))
- Bismuth Telluride (Bi2Te3(T))
-
Metal target material
-
Sputtering Target
-
- Services
- Media
- Partner
- Contact Us
- About
- Home
- Products
- Functional crystal
- N* crystal
- Iceland Spar
Iceland Spar
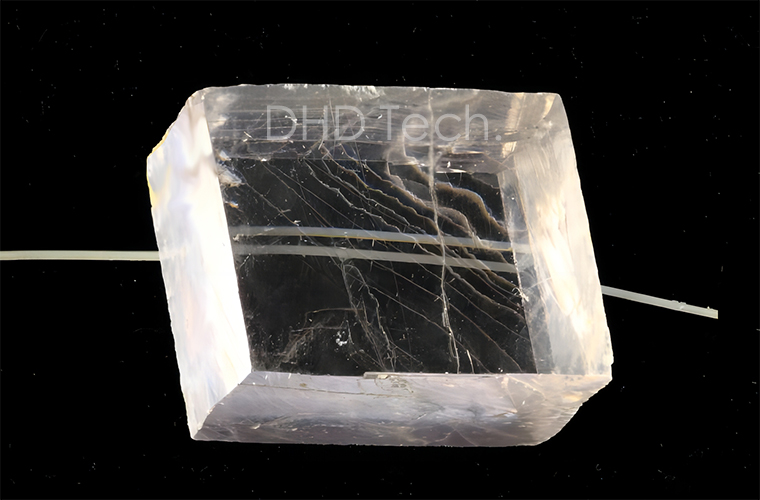
Iceland spar, or calcite, with a chemical composition of CaCO3, is a colorless, transparent, and pure calcite. Due to its special physical properties, it is called a special non-metallic mineral. It was first discovered in Iceland, hence it is called "Iceland Spar". It has the highest birefringence and polarization performance in white transparent crystal minerals. The crystals of high-quality ice spar are produced in the calcite veins of basalt and zeolite calcite veins. Mainly used in the national defense industry and manufacturing high-precision optical instruments, it is also widely used in technical fields such as radio electronics and astrophysics.
Applications
It can be used in the national defense industry and manufacturing high-precision optical instruments, and is also widely used in technical fields such as radio electronics and astrophysics.
Features
Calcite has good transparency, especially in the visible light range. This enables it to transmit light when manufacturing optical components, making it suitable for manufacturing transparent optical devices;
It can separate the different polarization states of incident light. This property is useful in some optical applications, such as manufacturing polarizers and waveplates;
Having good optical uniformity is crucial for manufacturing high-precision optical components;
It has a relatively high refractive index, which allows it to be used in some optical devices to focus light or enhance optical effects;
It has relatively high thermal stability, which makes it advantageous in some optical applications that require high-temperature resistance. Characteristics.
-
Crystal system: Tripartite crystal system;
Shape: rhombohedron;
Colors: colorless transparency, purple transparency, light yellow transparency, golden transparency, brown transparency, green transparency;
Optical properties: uniaxial crystal (-);
Refractive index: Ne=1.4864, No=1.6584( λ= 589nm);
Rebate rate: 0.1720;
Cleavage: rhombic cleavage {1011};
Double crystal: clustered twin {0112};
Fluorescence: None;
The Mohs hardness is 3;
Density: 2.703g/cm3-2.715g/cm3.
Colorless in thin films. Uniaxial crystals (-) are sometimes abnormal biaxial crystals. 2V=5-10 °. No=1.658, Ne=1.486. When similar to Mn and Fe, N increases.

